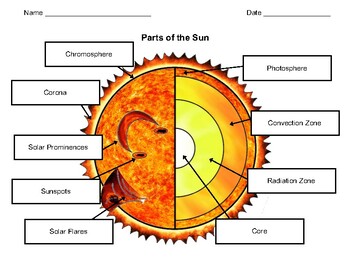
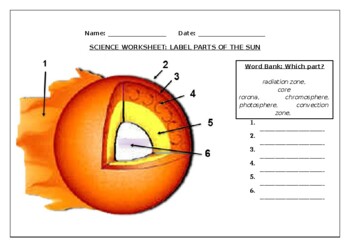
38 label the different areas of the sun
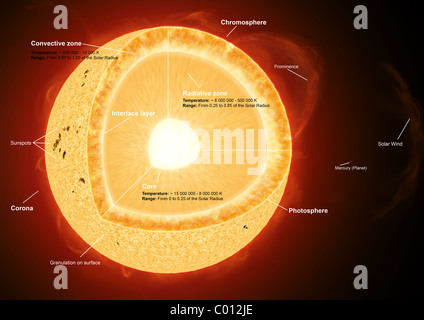
The sun's atmosphere: Photosphere, chromosphere and corona Since the sun is a ball of gas with no solid form, different regions rotate at different rates. The sun's equatorial regions rotate in about 24 days, while the polar regions take more than 30 days ... PDF The Sun Worksheet - Northland Preparatory Academy Unlike Earth, the sun does not have a solid surface. Like Earth, the sun has an interior and an atmosphere. The sun's interior consists of the core, radiation zone, and convection zone. Each layer has different properties. The sun produces an enormous amount of energy in its core, or central region. The sun's energy comes from nuclear fusion.
In Depth | Sun - NASA Solar System Exploration Since the Sun is not solid, different parts rotate at different rates. At the equator, the Sun spins around once about every 25 Earth days, but at its poles, the Sun rotates once on its axis every 36 Earth days. Moons. As a star, the Sun doesn't have any moons, but the planets and their moons orbit the Sun. Rings. Rings

Label the different areas of the sun
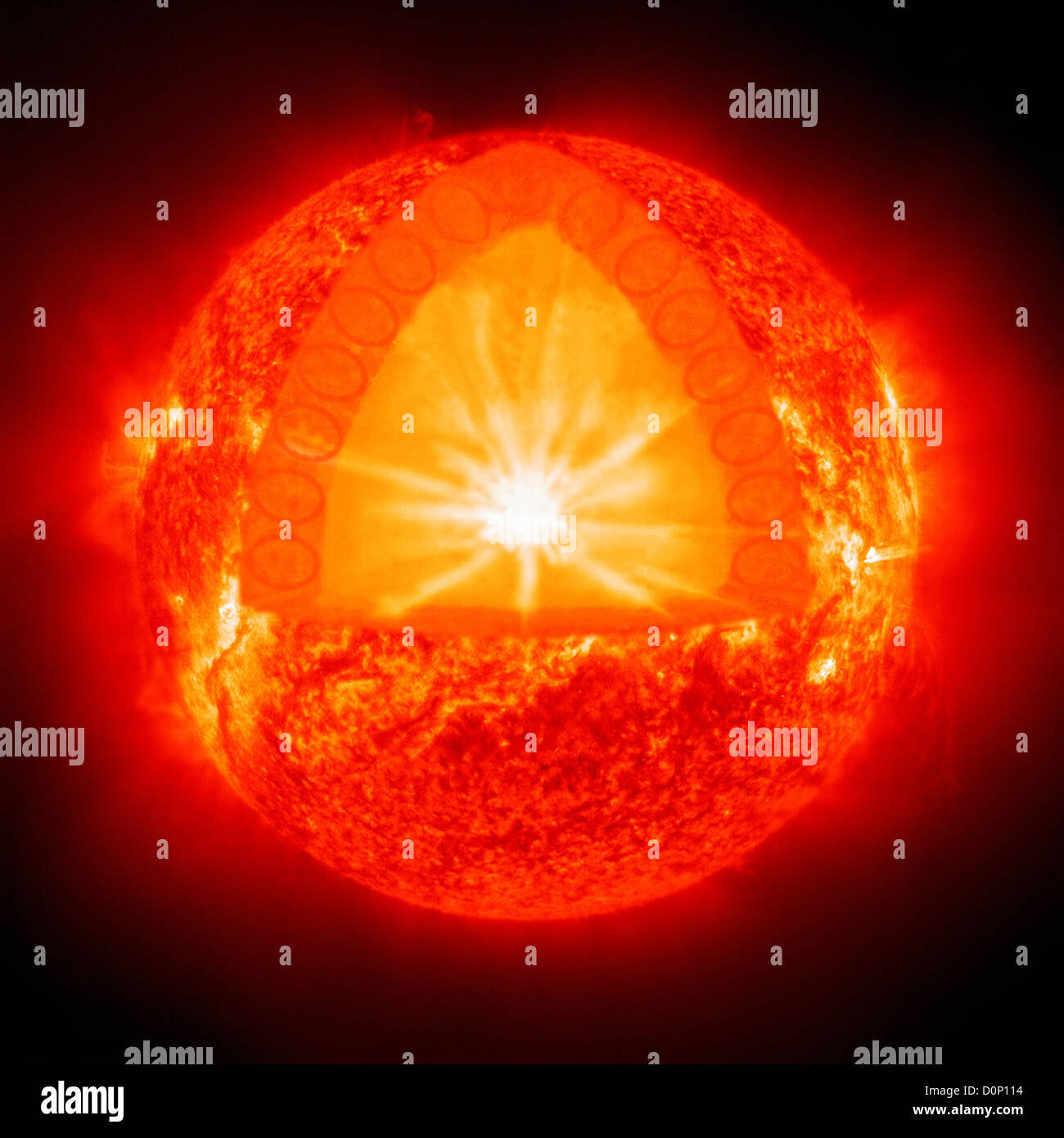
The Sun, Earth, and Cardinal Directions - National Geographic Society Cut out 10 large yellow paper suns from construction paper. On white construction paper, write in large letters north, south, east, and west. Put the words east and west on the east and west walls of the classroom. You can download a compass app on a smartphone or tablet to ensure correct placement of these. 2. Sun - Internal structure | Britannica The energy radiated by the Sun is produced during the conversion of hydrogen (H) atoms to helium (He). The Sun is at least 90 percent hydrogen by number of atoms, so the fuel is readily available. Since one hydrogen atom weighs 1.0078 atomic mass units and a single helium atom weighs 4.0026, the conversion of four hydrogen atoms to one helium atom yields 0.0294 mass unit, which are all ... The Structure and Composition of the Sun | Astronomy | | Course Hero Parts of the Sun: This illustration shows the different parts of the Sun, from the hot core where the energy is generated through regions where energy is transported outward, first by radiation, then by convection, and then out through the solar atmosphere. The parts of the atmosphere are also labeled the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona.
Label the different areas of the sun. PDF All About that Tilt: Sun and Seasons - NASA activity to see how the angle of the Sun affects your shadow. For example, if you were standing at 45ºN latitude, the noon Sun angle at summer solstice would be: 45° N - 23.5° N = 21.5° 90° - 21.5° = 68.5° is the noon Sun angle . Find these Sun angles: Noon Sun angle at equinoxes. 45° N - 0° N = 45° 90° - 45° = ____° is the ... The Sun - Imagine the Universe! The parts of the Sun that we can observe and measure directly are contained in the Sun's atmosphere: the photosphere, chromosphere and corona. These regions have substantially different properties from each other, with regions of gradual transition between them. Learn more about other parts of the Sun from the NASA's Solar System Exploration Division Anatomy of the Sun | NASA Anatomy of the Sun. The Sun's Core - Energy is generated via thermonuclear reactions creating extreme temperatures deep within the Sun's core. The Convection Zone - Energy continues to move toward the surface through convection currents of the heated and cooled gas. The Chromosphere - This relatively thin layer of the Sun is sculpted by ... Understanding Astronomy: The Sun and the Seasons - Weber State University The Sun from Different Latitudes. The sun's location with respect to the stars doesn't depend on your observing location on earth, so you now know enough to figure out how the sun appears to move through the sky from other locations. If you travel east or west, you'll see the sun rise and set earlier or later, respectively, just like a star would.
PDF Parts of the Sun - Solar Physics at MSU 1. Core: This is the center layer of the sun. This is where all the sun's heat and light is made. 2. Radiative Zone: The heat and light move from the core into this layer. 3. Convection Zone: In this layer, the gases move like boiling water. This moves them from the inner parts of the Sun to the outer part of the sun that we see. 4. "Parts" of the Sun | Center for Science Education Scientists who study the Sun usually divide it up into three main regions: the Sun's interior, the solar atmosphere, and the visible "surface" of the Sun which lies between the interior and the atmosphere. There are three main parts to the Sun's interior: the core, the radiative zone, and the convective zone. The core is at the center. PDF A Diagram of the Earth-Sun Relationship - Harvard University A Diagram of the Earth-Sun Relationship Notice that the Earth's tilt is always directed towards one place in space (in this model, it is towards the left. But notice all you need to do is move your perspective to underneath or some other side, and saying the pole tilts towards "the left" becomes meaningless. Anatomy of the Sun Diagram | Quizlet Photosphere It is the visible surface of the Sun. It appears relatively smooth except for occasional sunspots; an increase in the number, size, and complexity of these sunspots suggests unrest beneath this layer. Chromosphere It is a reddish gaseous layer immediately above the photosphere of the sun or another star.
Layers of the Sun - The Sun Today with Dr. C. Alex Young the solar interior composed of the core (which occupies the innermost quarter or so of the Sun's radius), the radiative zone, and the convective zone, then there is the visible surface known as the photosphere, the chromosphere, and finally the outermost layer, the corona. Earth's rotation around the Sun and the sequence of four seasons The Earth revolves around the Sun once every 365 and quarter days (one year), The rotation of the Earth around the Sun causes the sequence of the four seasons (the summer - the spring - the autumn - the winter). The sequence of the four seasons. The Earth's axis is inclined and this causes the difference in the length of the day and the ... Earth-Sun Relationships | National Geographic Society The amount of sun a region receives depends on the tilt of the earth's axis and not its distance from the sun. The northern hemisphere experiences summer during the months of June, July, and August because it is tilted toward the sun and receives the most direct sunlight. Inversely, summer for the southern hemisphere takes place during the months of December, January, and February because that is when it receives the most direct sunlight. What Are The Layers Of The Sun? - WorldAtlas The layers of the Sun are divided into two larger groups, the outer and the inner layers. The outer layers are the Corona, the Transition Region, the Chromosphere, and the Photosphere, while the inner layers are the Core, the Radiative Zone, and the Convection Zone. There are four outer layers of the Sun, and the Corona is the outermost one.
What are the Parts of the Sun? - Universe Today Radiative Zone: The radiative zone of the Sun starts at the edge of the core of the Sun (0.2 solar radii), and extends up to about 0.7 radii.Within the radiative zone, the solar material is hot ...
Layers of the Sun | NASA Layers of the Sun. This graphic shows a model of the layers of the Sun, with approximate mileage ranges for each layer: for the inner layers, the mileage is from the sun's core; for the outer layers, the mileage is from the sun's surface. The inner layers are the Core, Radiative Zone and Convection Zone. The outer layers are the Photosphere, the Chromosphere, the Transition Region and the Corona.
The Sun | Earth Science | | Course Hero The Sun (Figure below) is the center of the solar system and the largest object in the solar system. This nearby star provides light and heat and supports almost all life on Earth. ... The photosphere is relatively cool -- only about 6,700°C. The photosphere has several different colors; oranges, yellow and reds, giving it a grainy appearance ...
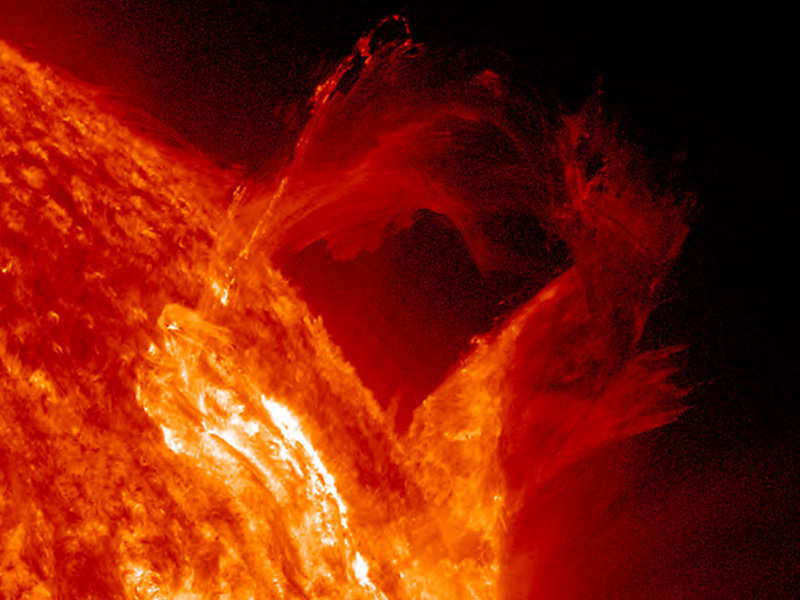
The Sun and Sunspots - National Weather Service Sunspots are areas where the magnetic field is about 2,500 times stronger than Earth's, much higher than anywhere else on the Sun. Because of the strong magnetic field, the magnetic pressure increases while the surrounding atmospheric pressure decreases. This in turn lowers the temperature relative to its surroundings because the concentrated ...
Sun - Earth Relationship: The Seasons | Earth Science - Lumen Learning The seasons are caused by the direction Earth's axis is pointing relative to the Sun. The Earth revolves around the Sun once each year and spins on its axis of rotation once each day. This axis of rotation is tilted 23.5 degrees relative to its plane of orbit around the Sun. The axis of rotation is pointed toward Polaris, the North Star.
How does the location of sunrise and sunset change throughout the year ... A similar circle which is separated from the first circle by 23.5 degrees at zenith towards south will mark the path of the Sun on winter solstice. Thus, the Sun will rise north of true East and set north of true West during summer whereas during winter, the Sun will rise south of true East and set south of true West.
Layers of the Sun | Parts of the Sun | DK Find Out The structure of the sun is made up of four layers. At the very center is the dense, hot core. Around the core lie two layers: a thick layer called the radiative zone and a thinner, cooler layer called the convective zone. Surrounding all of them is the sun's surface layer, known as the photosphere. Above this lies the sun's thin atmosphere, which is made up of the chromosphere and the corona.
Surface Features of the Sun ( Read ) | Earth Science Describes the surface features of the Sun, including sunspots, solar prominences, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections. Quick Tips. Notes/Highlights.
ASTRONOMY CH 11 Flashcards | Quizlet Label each region of the Sun with the most important process that is happening there. Rank the layers of the Sun in order from highest to lowest temperature. Rank the layers of the Sun in order from lowest to highest density. highest temperature 1. core 2. radiative zone 3. convective zone lowest temperature lowest density 1. convective zone
Layers of the Sun | Science Facts The Radiation Zone. The radiation zone is just outside the core. The function of this layer is to transfer energy from the core to the other layers. The temperature at this layer is cooler than the core at 7 million degrees Fahrenheit causing thermal radiation. This layer has 60 percent mass and 90 percent volume.
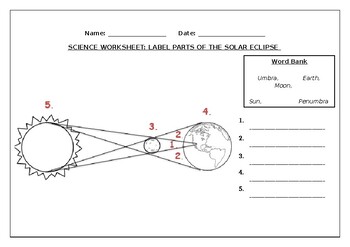
The diagram below shows the position of the sun, moon, and Earth. The ... The diagram below shows the position of the sun, moon, and Earth. The labels A, B, C, and D represent four coastlines on Earth. A D Earth B Moon Sun C As Earth rotates, coastline C moves to where coastline B is. ... It will experience a low tide because water is drawn away from the area between the high tides and the moon. D.) It will ...
The Structure and Composition of the Sun | Astronomy | | Course Hero Parts of the Sun: This illustration shows the different parts of the Sun, from the hot core where the energy is generated through regions where energy is transported outward, first by radiation, then by convection, and then out through the solar atmosphere. The parts of the atmosphere are also labeled the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona.
Sun - Internal structure | Britannica The energy radiated by the Sun is produced during the conversion of hydrogen (H) atoms to helium (He). The Sun is at least 90 percent hydrogen by number of atoms, so the fuel is readily available. Since one hydrogen atom weighs 1.0078 atomic mass units and a single helium atom weighs 4.0026, the conversion of four hydrogen atoms to one helium atom yields 0.0294 mass unit, which are all ...
The Sun, Earth, and Cardinal Directions - National Geographic Society Cut out 10 large yellow paper suns from construction paper. On white construction paper, write in large letters north, south, east, and west. Put the words east and west on the east and west walls of the classroom. You can download a compass app on a smartphone or tablet to ensure correct placement of these. 2.























Post a Comment for "38 label the different areas of the sun"