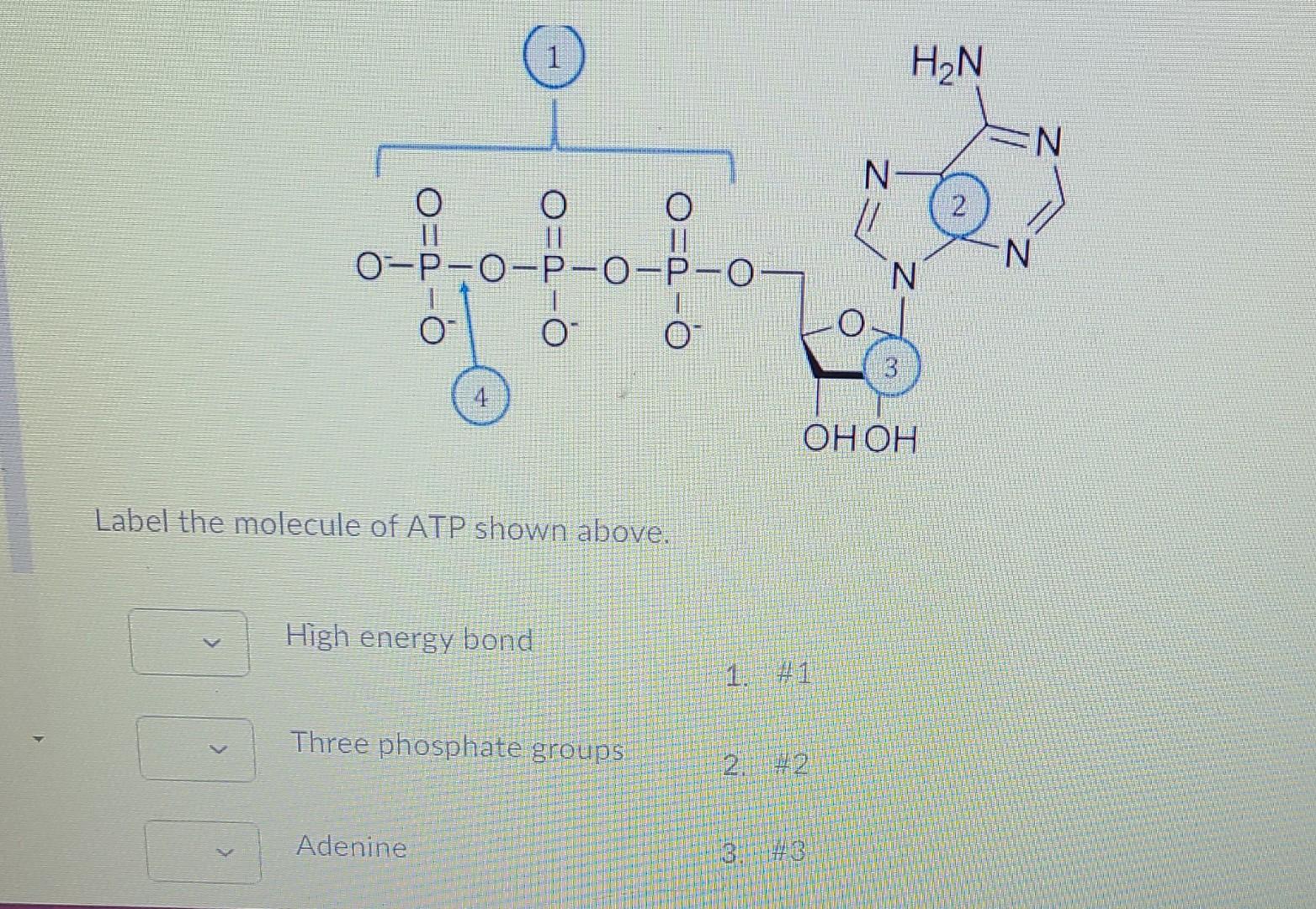
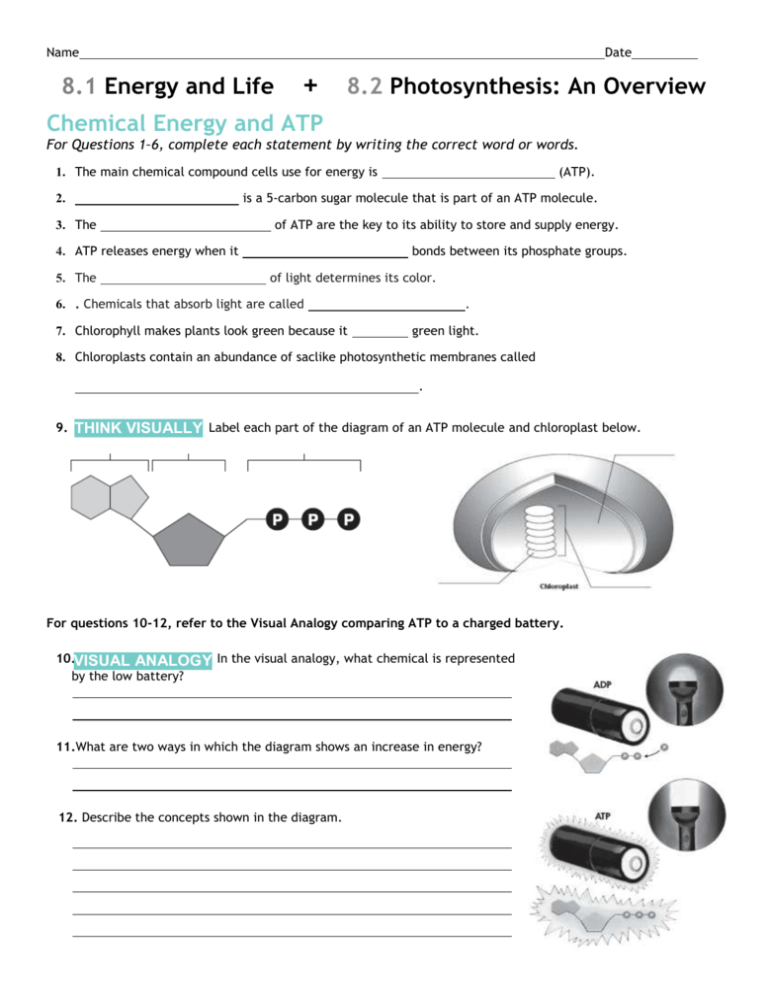
39 label the atp molecule below
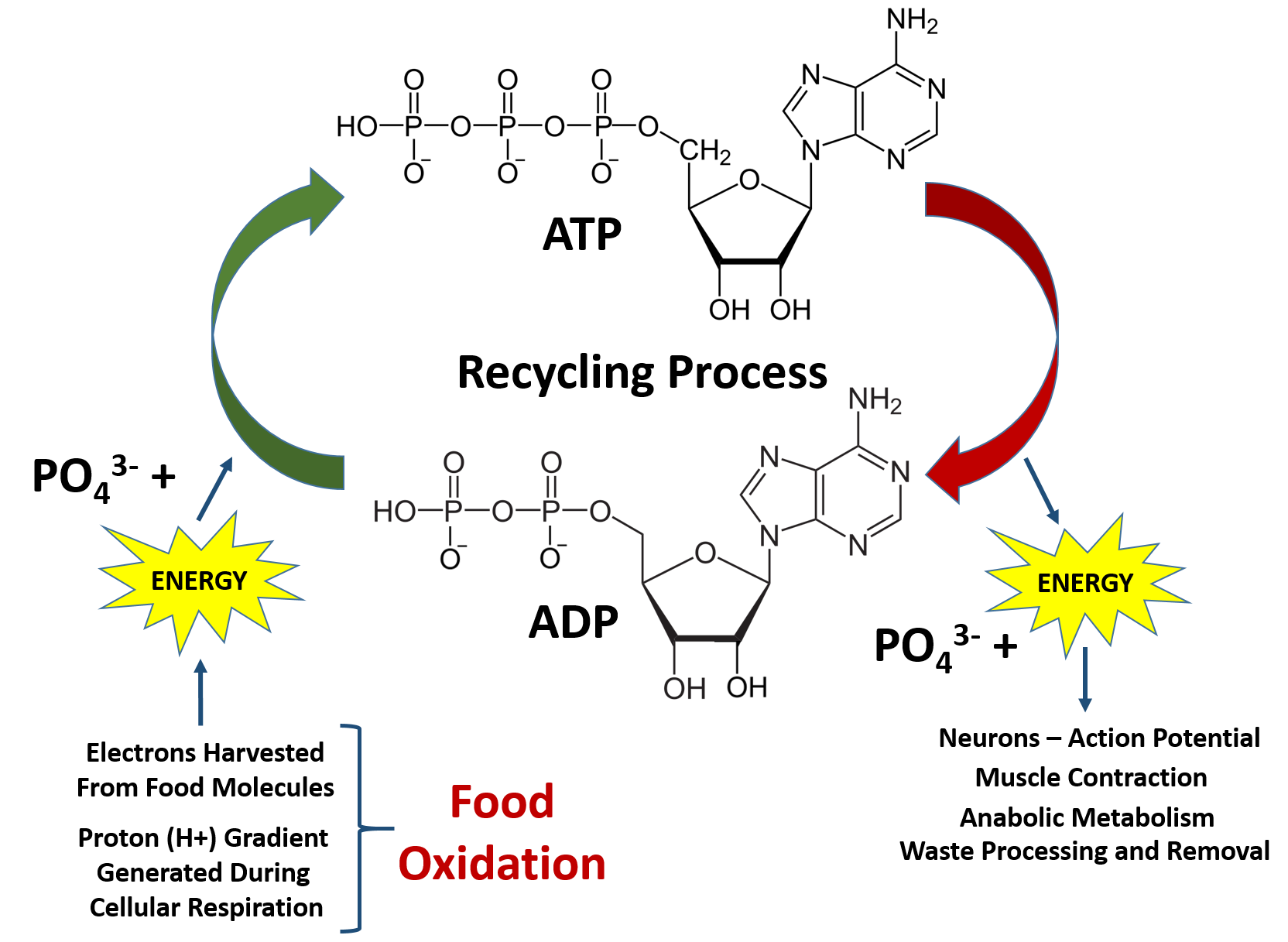
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP): Definition, Structure, Function Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is a chemical that transports energy throughout cells. It is the cell's primary energy currency, and it is produced as a by-product of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using light energy), cellular respiration, and fermentation. ATP is used by all living things. Photosynthesis: ATP and ADP Cycle - bealsscience ATP is one of the most important compounds inside a cell because it is the energy transport molecule. ATP (Adenosine TriPhosphate) is considered a transporter of energy because when one of the phosphate groups is broken off, turning it into Adenosine DiPhosphate (the Tri means 3 phosphate groups, the Di means 2 phosphate groups).
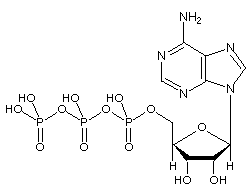
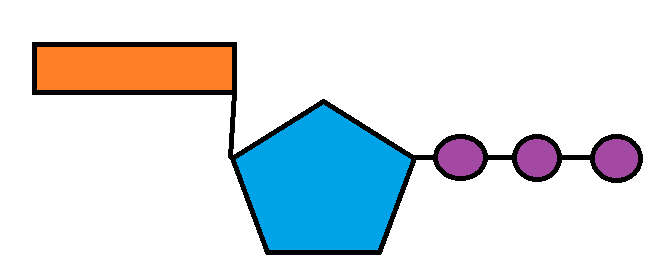
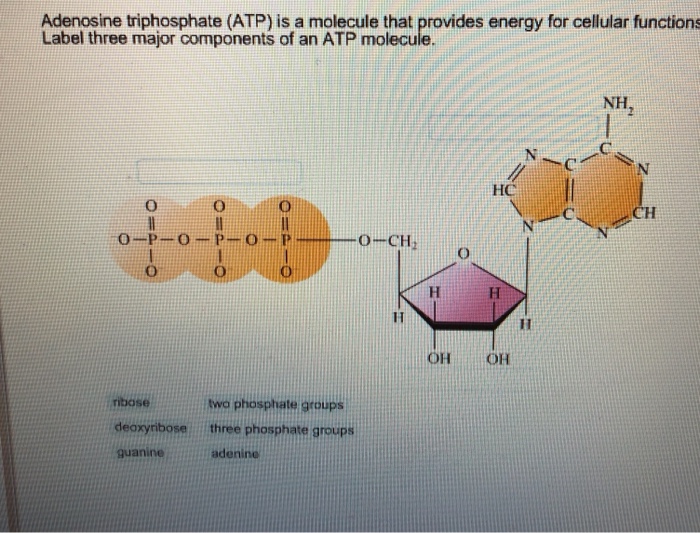
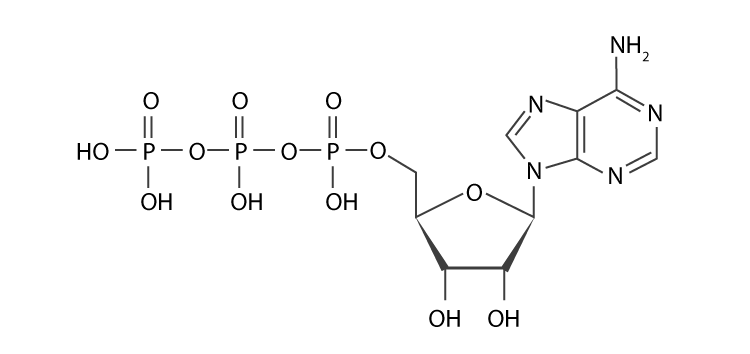
Answered: Part 1: The structure of ATP TP… | bartleby Part 1: The structure of ATP TP consists of 3 parts: I adenine molecule, I ribose sugar molecule, and 3 phosphate molecules. nergy is stored in the bond that is found between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. 1. COLOR the following ATP molecules below and provide a key to show the 3 parts. 2. Label the area that represents the HIGH ENERGY bond.
Label the atp molecule below
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture: atp molecule labeled - martatomsa.com The data table shows the carbon dioxide produced during the germination period of peas under different conditions. (B) AFM image of a Nanogold-labeled 500-base-long probe bound to a λ-DNA substrate molecule. If the carbons from glucose were radioactively labeled, what molecule(s) would end up with the label? Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive This model shows the structure of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. ATP has many important roles in the cell. A major role of ATP is to bind to and activate enzymes called kinases. Kinases catalyze the process of phosphorylation, which transfers a phosphate group from ATP to another ...
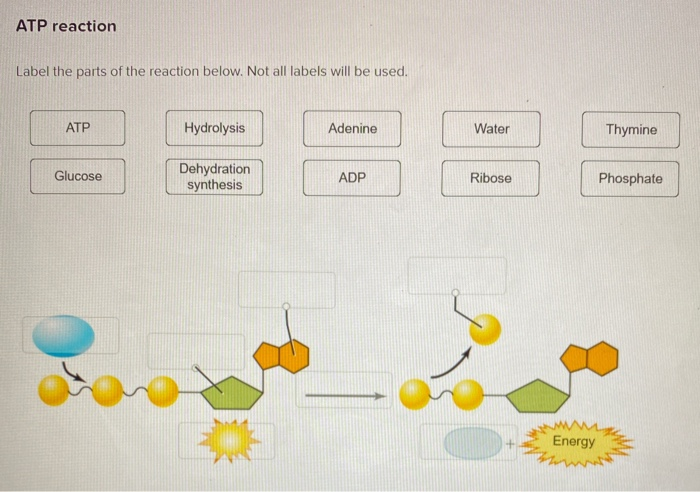
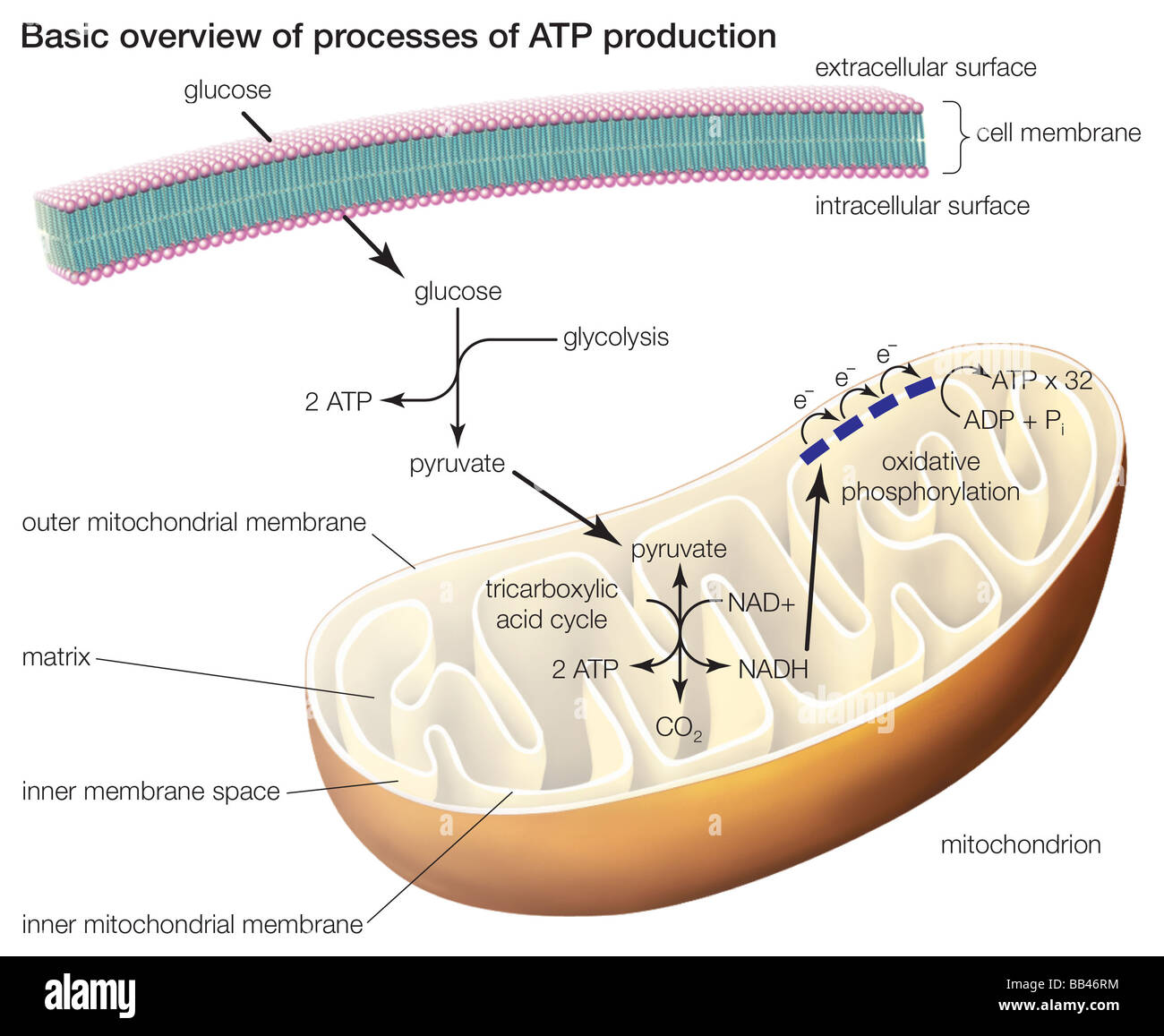
Label the atp molecule below. Р P- P 1. Label the ATP shown above. 2. Which part of the structure is ... In ATP molecules, energy is stored in the covalent bonds that is present between phosphates. The greatest amount of energy is present in the bond between the second and third phosphate groups. ADP is converted to ATP by the addition of a high-energy phosphate group to ADP making it ATP. ATP has more potential energy than ADP. Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below View Winter Horton - wksht 8.1 from BIO WEQ at San Marino High. Name Winter Horton Per 6 Date Oct. 1, 2019 Please type all your responses in BLUE or RED font. 8.1 Energy and Life Lesson Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The discovery of ATP was made by Karl Lohman (1929). ATP is a nucleotide consisting of a base-adenine, a pentose sugar-ribose and three phosphate groups. Out of three phosphate groups the last two are attached by high energy rich bonds (Figure 14.3). On hydrolysis, it releases energy (7.3 K cal or 30.6 KJ/ATP) and it is found in all living ... ATP Production - The Mitochondria Here are three steps before the ATP is created in the mitochondria. The first step is called Glycolysis. Then there is The Krebs Cycle and last there is the Electron Transport Chain before ATP is created. This part of the process of cellular respiration is where all the glucose is broken down and turned into two, three carbon molecules called ...
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule - Chegg Question: Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions &-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low battery? What arc two ways in which the diagram shows an increase in energy? Describe the concepts shown in the diagram. Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and... Answered: The molecule below is ATP. If you were… | bartleby Solution for The molecule below is ATP. If you were to buy radioactively labeled ATP to use in making radiolabeled RNA, which phosphate (indicate with an arrow)… Answered: The molecule below is ATP. biology honors: chapter 8 Flashcards | Quizlet H+ ions accumulate within the thylakoid space, the build up makes the stroma negatively charged, the difference in both charge and H+ ion concentration provides energy to make ATP, H+ ions cannot directly cross the thylakoid so the ATP synthase allows H+ ions to pass through it, H+ ions pass through ATP synthase and force it to rotate, while rotating ATP synthase binds ADP & a phosphate group together to make ATP
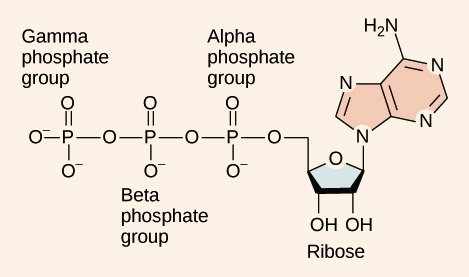
Color label the following in the atp molecules below COLOR LABEL the following in the ATP molecules below adenine red ribose orange 3 from SHS - 11 123 at Oro Site High School. Study Resources. Main Menu; by School; by Literature Title; ... Color label the following in the atp molecules below. School Oro Site High School; Course Title SHS - 11 123; Uploaded By GrandTree2552. The ATP molecule in 3-D - BioTopics The ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecule has 3 main parts: the base adenine - a double ring like section with several nitrogen atoms (blue), the 5 carbon sugar ribose in the centre, and 3 phosphate groups - a row of phosphorus atoms (orange) surrounded by oxygens (red). PDF worksheet chemical energy and ATP - frontiercsd.org 1. What type(s) of carbon-based molecules (organic compounds) are the source for most of the energy in the foods you eat? 2. Where is the energy stored in these molecules? 3. What is ATP? 4. What is ATP used for in cells? 5. Identify the parts of an ATP molecule below: (Label adenosine, ribose, and phosphate molecules) 6. Phosphorylation Basics - Sigma-Aldrich Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphoryl (PO 3) group to a molecule. In biological systems, this reaction is vital for the cellular storage and transfer of free energy using energy carrier molecules. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP), the most abundant energy carrier molecule, has two high-energy phosphate‑phosphate bonds that can be ...
Model of ATP Molecule | Perkins eLearning Preparation: Build an ATP Model First, build your five-carbon sugar, RIBOSE. Use five Popsicle sticks, and hot glue them into a pentagon. Then, hot glue cotton balls on each corner of the shape. Next, build the base, ADENINE. This is going to look like one pentagon and one hexagon stuck together on one side.
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. For 3-D Structure of this image using Jsmol Click here
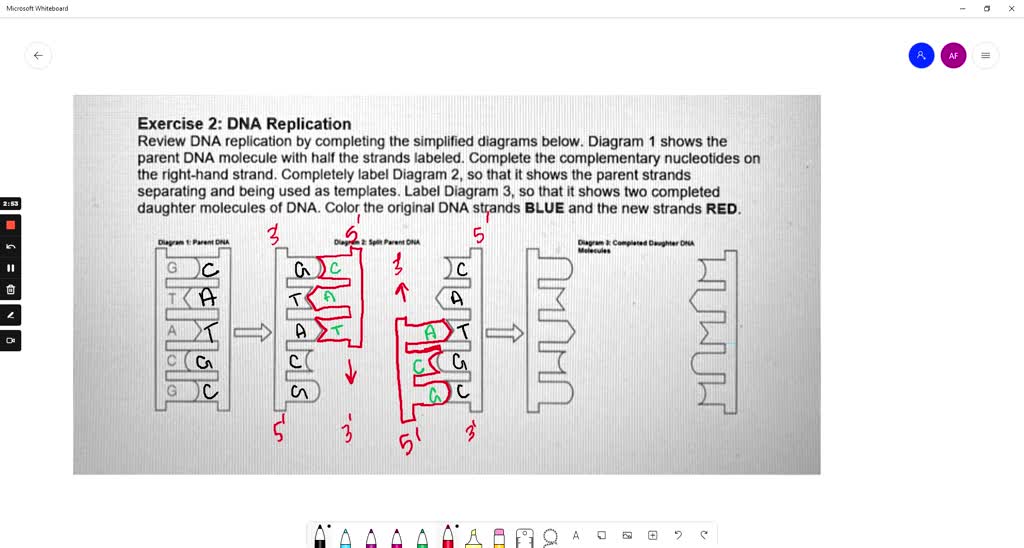
exercise 2 dna replication review dna replication by completing the simplified diagrams below diagram parent dna molecule with half the strands labeled complete the complementary nucleotides 86731
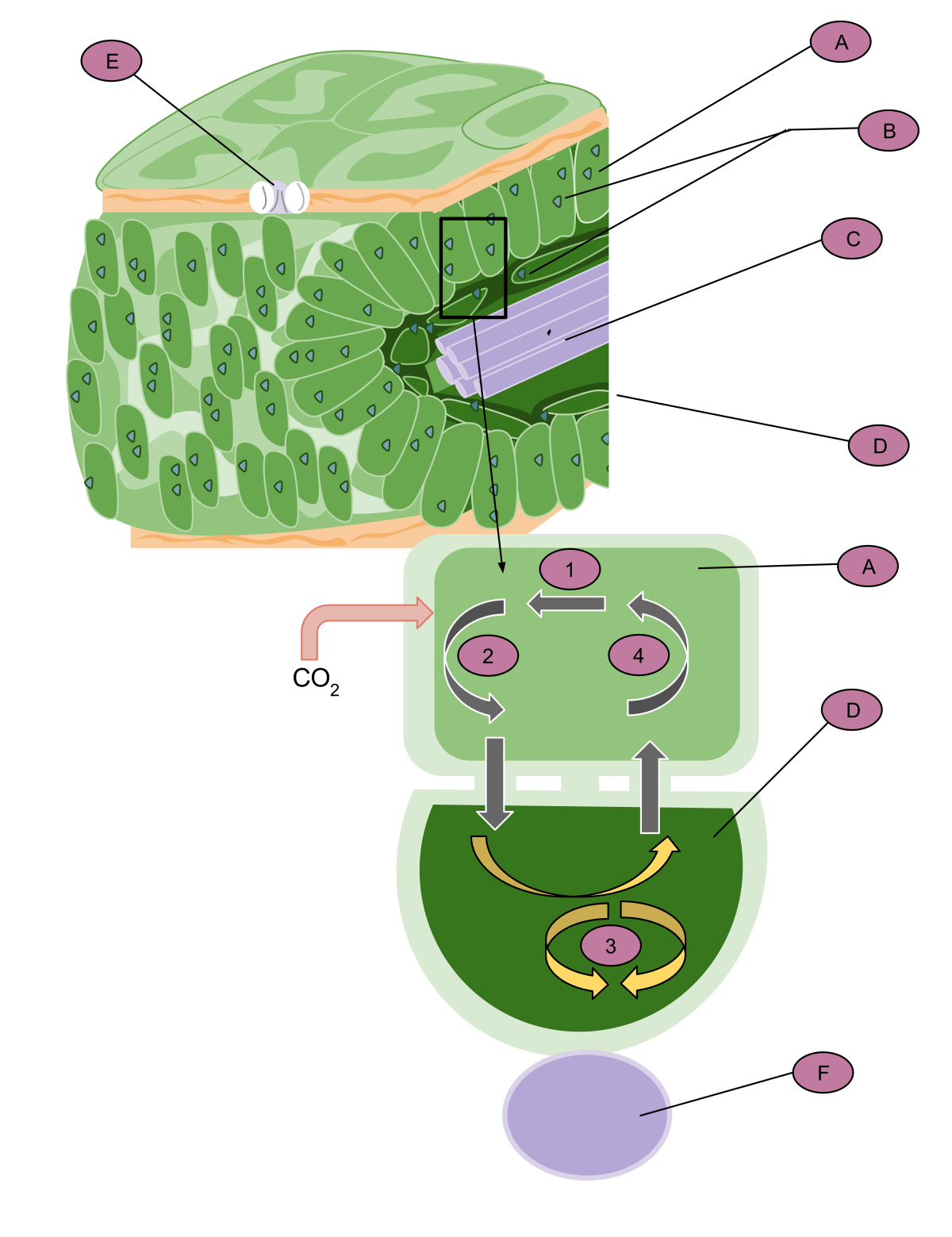
Chapter 3 Extra Credit Flashcards | Quizlet Label the figure below to investigate the effects of enzymes on chemical reaction rates Label the appropriate images in the ATP cycle. Label the figure below to assess your knowledge of the action of enzymes in biological cells.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP.
Solved Producing and using ATP Classify each label into the - Chegg Producing and using ATP Classify each label into the correct side in the diagram below. Breaking organic molecules into subunits Changing the shape of target molecules Endergonic reactions Building polymers Exergonic reactions 0 ADP.
Describe the three parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
atp molecule labeled - DaVinci Custom Linear Fireplaces Label each part of the atp molecule illustrated below. ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. What is atp an abbreviation for. n V (Ed. [6] Helicases may process much faster in vivo than in vitro due to the presence of accessory proteins that aid in the destabilization of the fork junction.
DOCX Ms. Grant's Bio Site - Home Part 1: The structure of ATP. ATP consists of 3 parts: 1 adenine molecule, 1 ribose sugar molecule, and 3 phosphate molecules. Energy is stored in the bond that is found between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. COLOR & LABEL the following in the ATP molecules below: adenine - red, ribose - orange, 3 phosphate groups - yellow. 3. 2. 1. 1. 2. 3
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams Cellular Respiration Equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 38*ATP. 10. Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, " biological machines " also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work. Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the ...
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive This model shows the structure of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. ATP has many important roles in the cell. A major role of ATP is to bind to and activate enzymes called kinases. Kinases catalyze the process of phosphorylation, which transfers a phosphate group from ATP to another ...
atp molecule labeled - martatomsa.com The data table shows the carbon dioxide produced during the germination period of peas under different conditions. (B) AFM image of a Nanogold-labeled 500-base-long probe bound to a λ-DNA substrate molecule. If the carbons from glucose were radioactively labeled, what molecule(s) would end up with the label?
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture:
















Post a Comment for "39 label the atp molecule below"