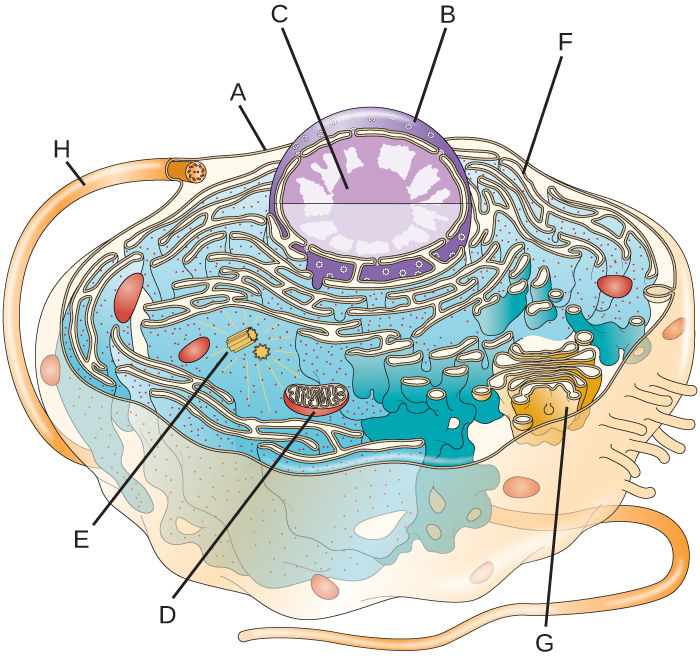
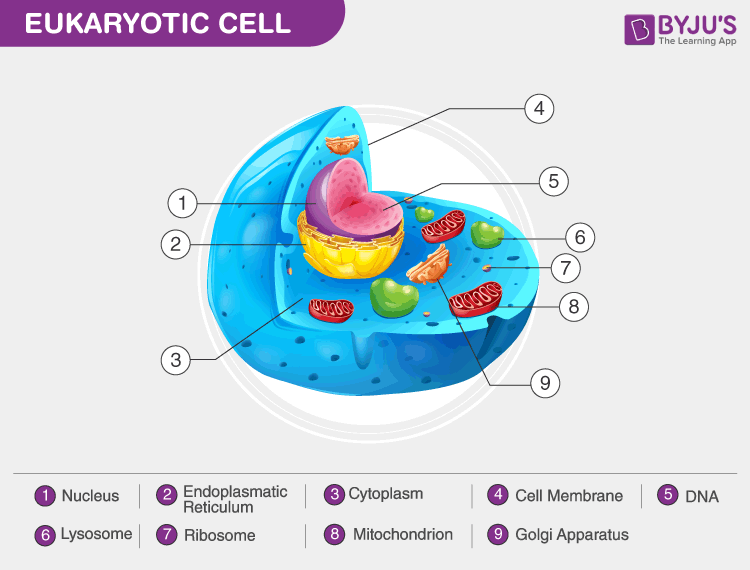
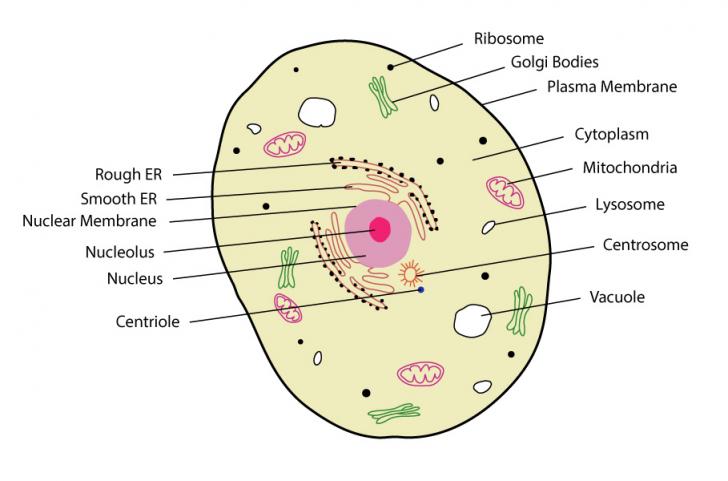
45 identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.
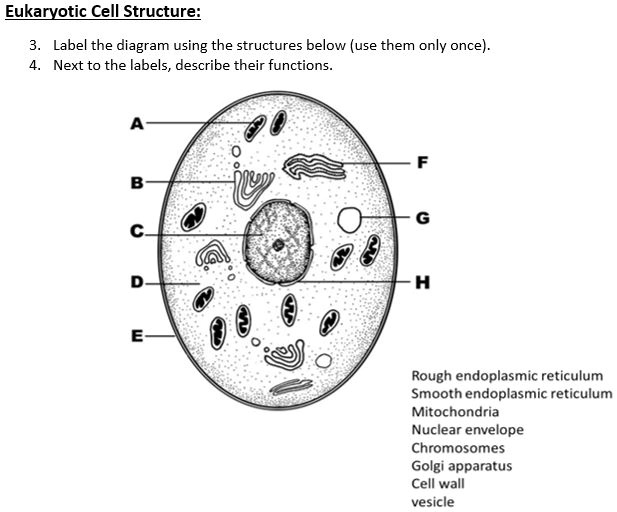
PDF Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells - Grosse Pointe Public Schools 1. Using the letters from the table in Model 1, label the cell diagram with the organelle names. 2. According to the table, a. what substance is analogous to a factory manager? b. in what organelle would this substance be found? 3. Using the information in Question 2, which cell organelle controls the activities of the entire cell? 4. Eukaryotic Cells- Definition, Characteristics, Structure ... - BYJUS Eukaryotic cells have the nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane. The cell has mitochondria. Flagella and cilia are the locomotory organs in a eukaryotic cell. A cell wall is the outermost layer of the eukaryotic cells. The cells divide by a process called mitosis. The eukaryotic cells contain a cytoskeletal structure.
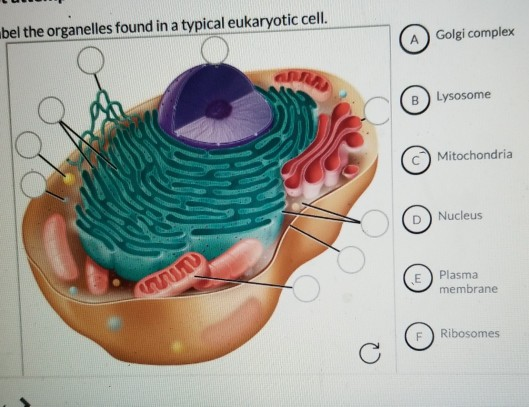
Solved Can you identify the cellular structures and their - Chegg Expert Answer. 100% (33 ratings) Transcribed image text: Can you identify the cellular structures and their functions in this diagram of a eukaryotic cell? ? Part A Drag the organelle labels to the appropriate pink targets. Then identify the function of each organelle on the blue target below it.
Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.
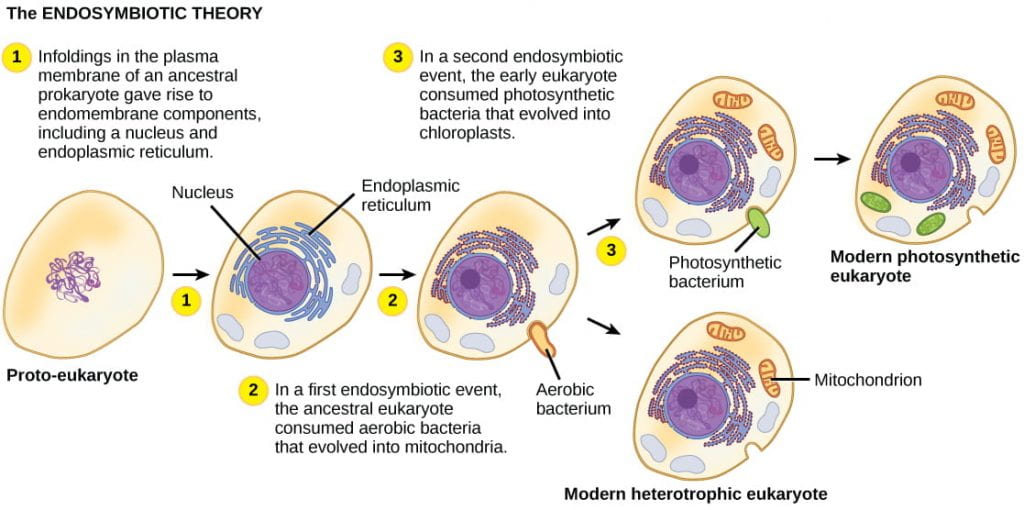
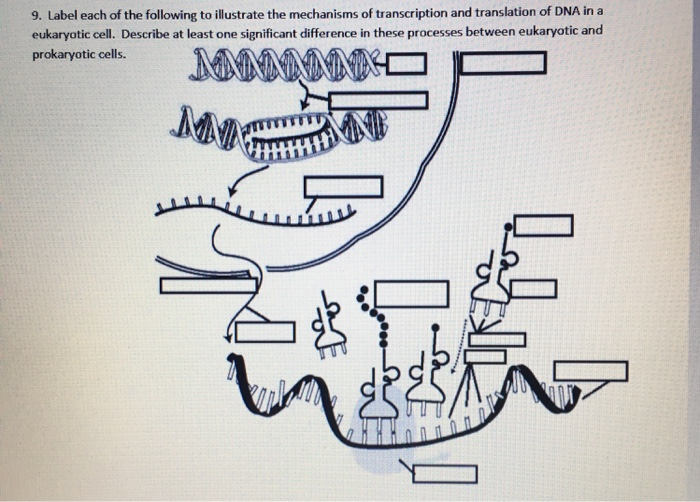
Solved In eukaryotic cells, the processes of protein | Chegg.com This problem has been solved! In eukaryotic cells, the processes of protein synthesis occur in different cellular locations. Drag the labels to the appropriate targets to identify where in the cell each process associated with protein synthesis takes place. RNA plays important roles in many cellular processes, particularly those associated with ... Eukaryotic Cells - Definition, Parts, Examples, and Structure Eukaryotic cells are defined as cells containing organized nucleus and organelles which are enveloped by membrane-bound organelles. Examples of eukaryotic cells are plants, animals, protists, fungi. Their genetic material is organized in chromosomes. Golgi apparatus, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Nucleus are parts of Eukaryotic Cells. Let's learn about the parts of eukaryotic cells in detail. The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Phases of the Cell Cycle. A typical eukaryotic cell cycle is illustrated by human cells in culture, which divide approximately every 24 hours. As viewed in the microscope, the cell cycle is divided into two basic parts: mitosis and interphase.Mitosis (nuclear division) is the most dramatic stage of the cell cycle, corresponding to the separation of daughter chromosomes and usually ending with ...
Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.. Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells - Course Hero Eukaryotic organisms include protozoans, algae, fungi, plants, and animals. Some eukaryotic cells are independent, single-celled microorganisms, whereas others are part of multicellular organisms. The cells of eukaryotic organisms have several distinguishing characteristics. Above all, eukaryotic cells are defined by the presence of a nucleus ... PDF Eukaryotic Cell Structure - Bellarmine University 5.2 Eukaryotic cell envelopes 1. Identify the types of eukaryotic microbes that have cell walls and distinguish them from plant cell walls. 2. Compare and contrast the cell envelopes of members of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya in terms of their component layers, molecular make-up, and function. 8 Anatomy and Physiology: Parts of a Human Cell - Visible Body You, dear reader, are a eukaryotic being. You are made up of trillions of eukaryotic cells, of which there are over 200 different types. Each eukaryotic cell type specializes to perform certain functions. Bone cells, for example, form and regenerate bones. Ever fracture a bone? Within days, cells called fibroblasts begin to lay down bone matrix. Eukaryotic Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells found in domains Archaea and Bacteria.
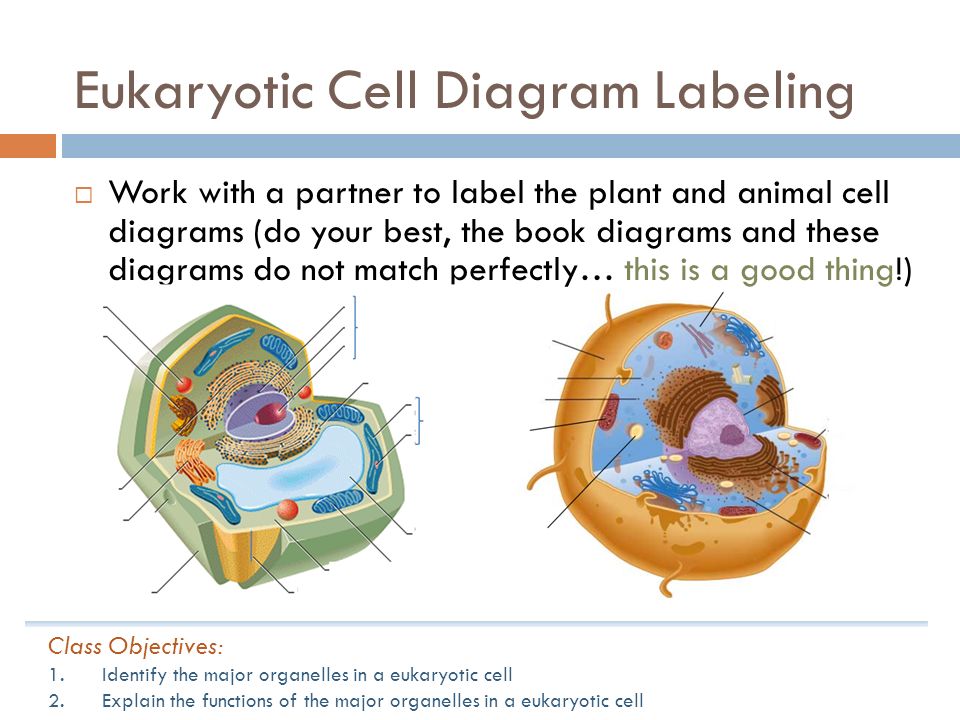
Cells | Biology I Laboratory Manual - Lumen Learning Draw three representative cells, each about 2 cm in diameter. Label one cell with structures listed above. What purpose do epithelial cells serve? Part 2: Plant Cells. There are two fundamental cell types: Parenchyma: These cells have thin walls, allowing free transfer of materials between membranes of adjacent cells. Major functions include ... Label Eukaryotic Cell Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Label Eukaryotic Cell. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, Structure & Function (with ... - Sciencing The Cytoplasm. In cell biology, each eukaryotic cell is separated into two categories: the nucleus, which we just described above, and the cytoplasm, which is, well, everything else. The cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells contains the other membrane-bound organelles we'll discuss below. What Helps Identify Cell Types - Realonomics How you identify cell All cells have continuous cell membrane that surrounds them and the cell membrane encloses number other tiny structures. ... For example the cell in Column "C" in Row "3" would be cell C3. Cells may contain Labels Numbers Formulas or Functions. ... A cell has three main parts: the cell membrane the nucleus and the ...
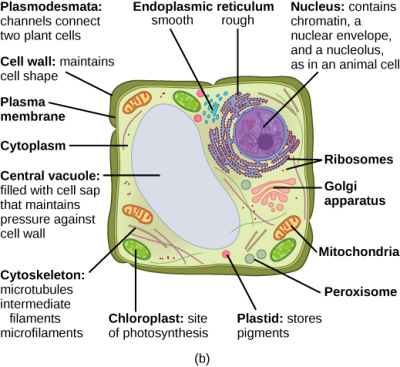
Eukaryotic Cells - Visible Body 1. Plant and animal cells are eukaryotic, meaning that they have nuclei. Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They generally have a nucleus—an organelle surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope—where DNA is stored.There are a few exceptions to this generalization, such as human red blood cells, which don't have a nucleus when mature. Eukaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram - Science Prof Online Eukaryotic Cell Envelope & External Structures. Cell Wall: The cells of plants, algae and fungi have thick, protective cell walls, which provide support, help maintain the shape of the cell, and prevent the cell from taking in too much fresh water and bursting. Plasma Membrane: All cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, have a plasma membrane, made mainly of phospholipids and proteins, which functions as a barrier, regulating the movement of materials between the inside and the outside of ... Learn the parts of a cell with diagrams and cell quizzes - Kenhub The first is the cell nucleus, which houses DNA in the form of chromosomes. The second is the cytoplasm, a thick solution mainly comprised of water, salts, and proteins. The parts of a eukaryotic cell responsible for maintaining cell homeostasis, known as organelles, are located within the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic Cells | Biology I - Lumen Learning Like a prokaryotic cell, a eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes, but a eukaryotic cell is typically larger than a prokaryotic cell, has a true nucleus (meaning its DNA is surrounded by a membrane), and has other membrane-bound organelles that allow for compartmentalization of functions.
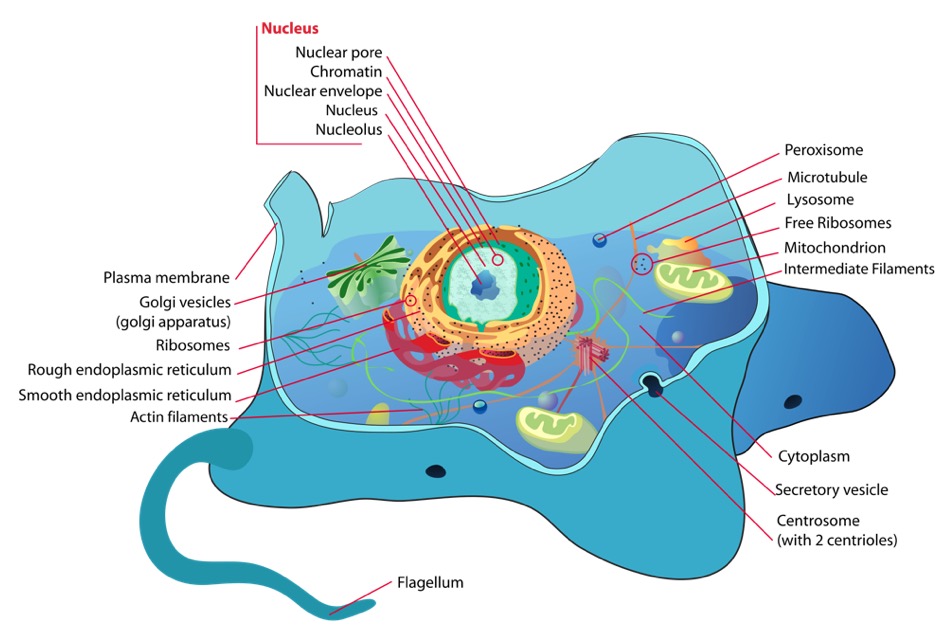
PDF 1 SECTION 2 Eukaryotic Cells - LAB RATKOS Eukaryotic Cells continued TAKE A LOOK 6. Identify Label the diagram of a nucleus using these terms: pore, DNA, nucleolus, double membrane. READING CHECK 7. Compare What is the difference between smooth ER and rough ER? Ribosome This organelle is where amino acids are hooked together to make proteins. NUCLEUS
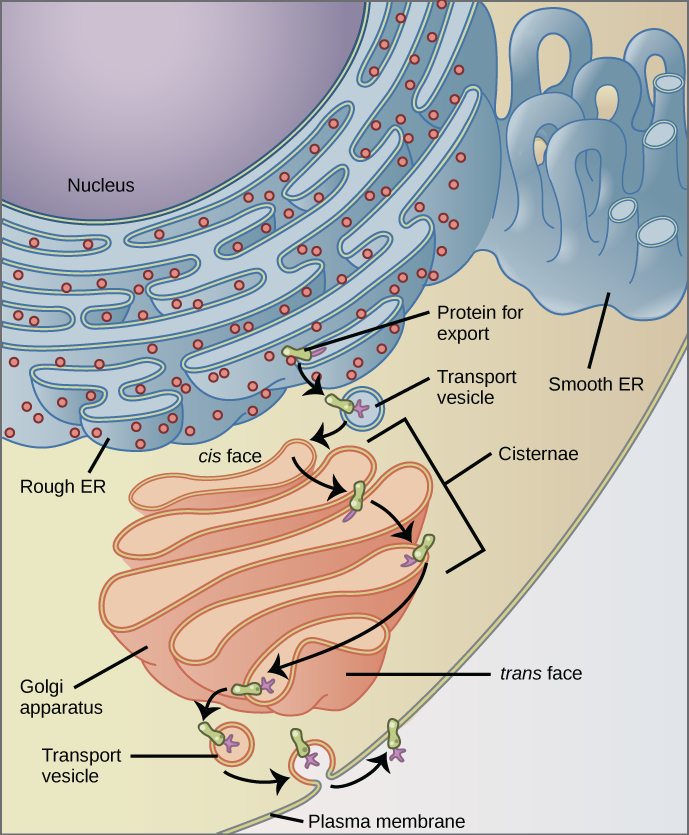
3.3 Eukaryotic Cells - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition The endomembrane system ( endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly.
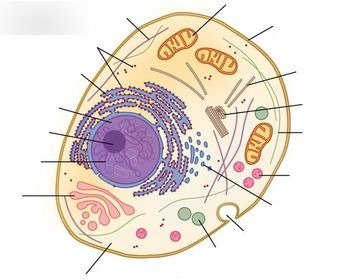
identify and label each part of the eukaryotic cell - Brainly.com Major parts of the eukaryotic animal cell are the nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, Golgi, ER, etc. What are animal cells? Animal cells are eukaryotes that lack cell walls but have almost the same components as plant cells. The cytoplasm is the component of the cell where all the organelle lies.
identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell - Brainly.com Label A nucleus. Label B cytoplasm. Label C ribosomes. Label D DNA. Label E cell membrane. Explanation: it's right on Edenuity
Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram The plant cell, being a eukaryotic cell, has large complex ribosomes with higher S units, with four rRNAs with over 80 proteins. The large subunit has the S unit of the 60s (28s rRNA, 5.8s rRNA, and 5s rRNA) with 42 proteins. The small subunit has a sedimentation rate of the 40s, made up one rRNA and 33 proteins.
Eukaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram - P3 - Science Prof Online Other Eukaryotic Cell Components and Organelles. Cytoplasm: The inside of the cell, between the nucleus and plasma membrane, is filled with a gel-like fluid in which the organelles are suspended. Cytoplasm includes both the liquid (called cytosol) and the suspended organelles. Cytoskeleton: Composed of microtubules, intermediate filaments and ...
A Well-labelled Diagram Of Animal Cell With Explanation - BYJUS There are various organelles present within the cell and are classified into three categories based on the presence or absence of membrane. Listed below are the Cell Organelles of an animal cell along with their functions. The cell membrane is a double-layered membrane made up of phospholipids that surrounds the entire cell. The membrane is selectively permeable and allows only certain molecules to pass through.
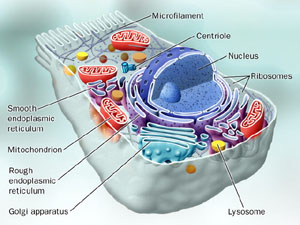
Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells - Windows to the Universe The "brains" of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA. Mitochondria. Make energy out of food. Ribosomes. Make protein. Golgi Apparatus. Make, process and package proteins. Lysosome. Contains digestive enzymes to help break food down.
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure, Characteristics & Diagram - Embibe Eukaryotic cell refers to the cell whose genetic material is surrounded by the nuclear membrane, i.e. has a well-defined nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. "Eu" means true and "karyon" means nucleus. Eukaryotic Cell: Characteristics All living organisms are made of cells.
Eukaryotic Cell Labeling Diagram | Quizlet Nuclear Envelope ... Nucleus ... Chromatin ... Nucleus ... Ribosomes ... Golgi Apparatus ... Lysosome ... Mitochondira ... Peroxisome ... Microvilli ... Microtubules ... Intermediate Filaments ... Microfilaments ... Cytoskeleton ... Centrosome ...
The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Phases of the Cell Cycle. A typical eukaryotic cell cycle is illustrated by human cells in culture, which divide approximately every 24 hours. As viewed in the microscope, the cell cycle is divided into two basic parts: mitosis and interphase.Mitosis (nuclear division) is the most dramatic stage of the cell cycle, corresponding to the separation of daughter chromosomes and usually ending with ...
Eukaryotic Cells - Definition, Parts, Examples, and Structure Eukaryotic cells are defined as cells containing organized nucleus and organelles which are enveloped by membrane-bound organelles. Examples of eukaryotic cells are plants, animals, protists, fungi. Their genetic material is organized in chromosomes. Golgi apparatus, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Nucleus are parts of Eukaryotic Cells. Let's learn about the parts of eukaryotic cells in detail.
Solved In eukaryotic cells, the processes of protein | Chegg.com This problem has been solved! In eukaryotic cells, the processes of protein synthesis occur in different cellular locations. Drag the labels to the appropriate targets to identify where in the cell each process associated with protein synthesis takes place. RNA plays important roles in many cellular processes, particularly those associated with ...








![Answered] Draw a plant cell and label the parts which a ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/dcf/6afccfe6260c9fea1ec344bf6369bb2f.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cell-membrane-373364_final-5b5f300546e0fb008271ce52.png)



:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12788/histology-eukaryotic-cell_english.jpg)





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/animal-cells-vs-plant-cells-373375_final-5b462d7fc9e77c00375014f1.png)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-prokaryotes-and-eukaryotes-129478-v41-5b69b4c546e0fb0025628d06.png)
Post a Comment for "45 identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell."